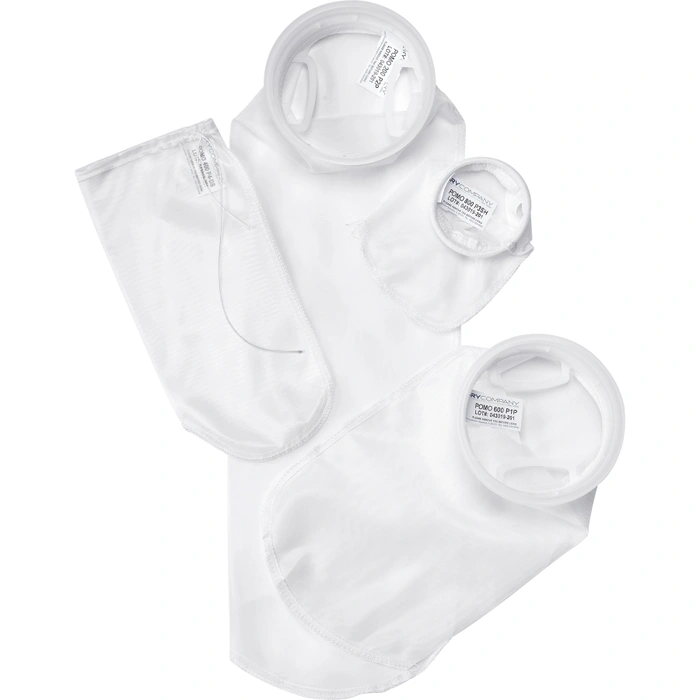
Unlock Precision Filtration with Polypropylene Monofilament Mesh Liquid Filter Bags
Polypropylene Monofilament Mesh Liquid Filter Bags provide unmatched surface‑flow filtration, combining precise pore size control, low pressure drop, and robust chemical resistance. By selecting the correct micron rating, collar style, and maintenan
When process streams demand high‑clarity and precise particle retention—whether you’re manufacturing pharmaceuticals, refining chemicals, producing beverages, or protecting sensitive equipment—a Polypropylene Monofilament Mesh Liquid Filter Bag delivers exceptional performance. Engineered for uniform pore size and minimal fiber migration, these bags offer reliable, reproducible filtration down to tight micron ratings. This guide follows a proven structure—market overview, product fundamentals, key features, selection advice, maintenance best practices, reasons to choose our solution, illustrative use cases, and actionable next steps—to help you harness the full potential of monofilament mesh filtration.

Market Overview: The Rise of Monofilament Mesh Filtration
Across industries, filtration needs have evolved beyond simple depth media to demand consistent, surface‑flow precision:
-
High‑Purity Requirements
Pharmaceutical, biotech, and microelectronics sectors require tight control over particle size; even nominal depth filters can shed fibers or yield variability. -
Consistent Pore Structure
Woven monofilament mesh offers uniform openings with minimal variability, ensuring every bag performs to the same standard—critical for batch‑sensitive processes. -
Low Particle Shedding
Unlike felt or staple fiber media, monofilament mesh maintains structural integrity under shear, minimizing downstream contamination. -
Easy Cleanability and Reuse
Smooth polypropylene strands resist fouling and facilitate backwashing or chemical cleaning, extending service life and reducing operational cost. -
Broad Chemical Compatibility
Polypropylene resists acids, alkalis, most solvents, and biological media, serving diverse process streams from aggressive chemicals to food‑grade liquids.
Understanding these drivers clarifies why many operations choose monofilament mesh filter bags for precision liquid filtration.
Understanding Polypropylene Monofilament Mesh Filter Bags
A Polypropylene Monofilament Mesh Liquid Filter Bag is a cylindrical bag woven from single‑strand polypropylene yarns, creating a stable grid of precisely sized openings. Unlike depth‑filtration felt bags, monofilament mesh filters operate by surface sieving: particles larger than the mesh openings are retained on the mesh face, while fluid flows through cleanly.
Core Components:
-
Mesh Construction: Woven monofilament strands define consistent, nominal or absolute pore sizes (e.g., 10 µm, 25 µm, 50 µm).
-
Bag Size & Dimensions: Standard Size 1 and Size 2 configurations (4″ × 10″ or 4″ × 20″) fit common housings; custom lengths available.
-
Top Closure: Sewn or molded collars—often F‑flange, snap band, or cap—ensure a leak‑free seal in filter vessels.
-
Support Cage (Optional): For high ΔP applications, internal cages prevent bag collapse and maintain maximum flow area.
Surface‑flow capture prevents deep media fouling, simplifies cleaning, and delivers predictable service life.
Key Features of Polypropylene Monofilament Mesh Bags
When evaluating monofilament mesh filter bags, look for these critical attributes:
1. Precision Pore Size
-
Nominal vs. Absolute Ratings: Choose nominal mesh for general particle control (85–95% capture) or absolute for ≥99.9% retention at rated size.
-
Wide Range of Micron Sizes: From ultra‑fine (1–5 µm) to coarse (100–200 µm), enabling tailored capture across applications.
2. High Flow Capacity & Low Pressure Drop
-
Surface Flow Design: Particles accumulate on the mesh exterior, preserving full open area underneath for continued high throughput.
-
Optimized Weave Patterns: Balanced open area and strand thickness minimize ΔP even at elevated flow rates.
3. Excellent Chemical Resistance
-
Polypropylene Media: Resists strong acids, bases, alcohols, and many solvents; ideal for industrial, food‑grade, and biological fluids.
-
FDA‑Compliant Options: For food, beverage, and pharmaceutical use, meet CFR‑21 and NSF standards.
4. Robust Mechanical Integrity
-
Tensile Strength: Monofilament strands maintain shape under differential pressures up to housing ratings, resisting deformation and sag.
-
Abrasion Resistance: Smooth surfaces reduce fiber wear under cyclic flows, ensuring consistent performance.
5. Cleanability & Reusability
-
Backwashing Capability: Surface‑trapped solids can be flushed away using reverse flow or gentle detergent washes.
-
Autoclavable/Steam‑Sterilizable: Certain polypropylene constructions endure repeated sterilization cycles, extending bag life in critical processes.
6. Secure Sealing & Fit
-
Precision‑Molded Collars: F‑flange or snap‑band collars guarantee tight seating, preventing bypass and ensuring all liquid passes through the mesh.
-
Dimensional Tolerance: Consistent OD and ID maintain uniform seal pressure in filter housings.
By combining these features, polypropylene monofilament mesh bags deliver reliable, high‑precision filtration across a wide array of process demands.
Choosing the Right Monofilament Mesh Bag
Selecting the optimal filter bag involves aligning mesh specifications and operational parameters with your process needs:
A. Define Required Micron Rating
-
Bulk Solid Removal: 50–100 µm nominal mesh for coarse debris and sediment control.
-
Intermediate Polishing: 5–25 µm nominal or absolute mesh for finer particulates and turbidity reduction.
-
Critical Applications: 1–3 µm absolute mesh for pre‑sterilization or ultra‑pure fluid requirements.
B. Match Flow Rate & Housing Size
-
Flow Demand: Standard Size 2 bags handle up to 10–20 GPM; for higher flows, consider multi‑bag housings or larger bag sizes.
-
ΔP Constraints: Ensure total flow and expected solids load maintain ΔP below housing collapse ratings (commonly 50–75 psi).
C. Evaluate Fluid Chemistry & Temperature
-
Aggressive Chemicals: Polypropylene excels in pH ranges 2–12 and temperatures up to 180 °F; for hotter streams, consult Teflon‑coated mesh or alternative polymers.
-
Food/Pharma: Select FDA‑grade mesh and collars to maintain purity standards.
D. Determine Maintenance Strategy
-
Disposable vs. Reusable: Budget, process cleanliness, and contamination risk dictate whether bags are single‑use or cleaned in place.
-
Cleaning Protocols: Validate backflush, chemical soak, or steam‑sterilization methods to ensure complete solids removal and media integrity.
E. Ensure Housing Compatibility
-
Collar Style: F‑flange, snap‑band, or cap‑style collars must match your filter vessel’s support ring design.
-
Dimensional Fit: Verify length and OD tolerances to prevent bypass and ensure seal integrity.
By carefully considering micron rating, flow, chemistry, maintenance, and housing fit, you’ll select a monofilament mesh bag that optimizes both performance and cost.
Maintenance and Best Practices
Implementing proper upkeep routines maximizes bag life and preserves filtration efficiency:
1. Monitor Differential Pressure
-
Pressure Gauges: Install gauges upstream and downstream of the housing; rising ΔP signals solids buildup.
-
Changeout Threshold: Define ΔP limits (e.g., 15–25 psi) to trigger cleaning or replacement before bypass occurs.
2. Cleaning & Reuse
-
Backwashing: Initiate gentle reverse flow at ≤25% operating pressure to dislodge particles without damaging mesh.
-
Detergent Soak: For oily or emulsified solids, soak bags in mild alkaline cleaners, rinse thoroughly, and air‑dry.
-
Sterilization: Autoclave or steam‑sterilize FDA‑grade bags for reuse in sterile processes.
3. Replacement Protocols
-
Disposable Use: Replace installed bags at scheduled intervals or when ΔP remains high after cleaning.
-
Inspection: Examine used bags for mesh tears or collar damage before reinstallation.
4. Housing Maintenance
-
O‑Ring & Gasket Care: Inspect and replace seals regularly to maintain leak‑free service.
-
Housing Cleaning: Wipe internal surfaces and support cages when changing bags to remove settled solids.
5. Documentation & Optimization
-
Record Parameters: Log bag life, total volume filtered, ΔP profiles, and cleaning cycles to refine schedules.
-
Performance Audits: Periodically test filtrate clarity or particle counts to verify bag efficacy.
Consistent maintenance practices preserve bag performance and protect your systems.
Why Choose Our Polypropylene Monofilament Mesh Bags
Our monofilament mesh filter bags excel through:
Premium Polypropylene Monofilament
-
High‑Purity Fibers: Single‑strand construction ensures uniform pore size, minimal fiber breakage, and low extractables.
Wide Micron Range & Rating Certainty
-
Nominal & Absolute: Offering both classifications, we guarantee performance to meet diverse application demands.
Robust Collar Designs
-
F‑Flange & Snap‑Band Options: Precisely molded collars for secure, bypass‑free fits in all standard housings.
High Flow, Low ΔP Profiles
-
Optimized Weave Patterns: Balances open area with mechanical strength to maintain minimal pressure drop.
Chemical & Thermal Resistance
-
Polypropylene Media: Stable in aggressive chemistries, temperatures up to 180 °F, and compatible with food/pharma applications.
Reusable & Disposable Lines
-
Versatile Use Models: Choose disposable economy or washable premium bags for cost‑effective operations.
Rigorous Quality Control
-
Batch Testing: Each lot undergoes dimensional, flow, and retention testing to ensure consistent performance.
By combining precision materials, expert design, and stringent quality checks, our monofilament mesh bags deliver reliable, high‑precision filtration that protects your processes and products.
Illustrative Use Cases
Use Case 1: Pharmaceutical API Filtration
A pharmaceutical facility installed 1 µm absolute monofilament bags ahead of final sterile filtration. Consistent mesh retention prevented downstream membrane fouling and ensured product sterility, reducing batch discard rates by 20%.
Use Case 2: Microelectronics Rinse Tanks
A semiconductor fab used 0.5 µm monofilament mesh socks to polish ultrapure water. The smooth surface allowed easy cleaning, maintaining sub‑ppt particle levels essential for wafer processing.
Use Case 3: Beverage Clarity Enhancement
A craft brewery employed 25 µm monofilament bags to remove hop and grain residues before final packaging. Rapid changeouts and washable bags cut filter change costs by 30% while preserving beer flavor.
Use Case 4: Industrial Paint Recirculation
A coatings manufacturer filtered paint recirculation loops with 50 µm bags, removing pigment agglomerates and preventing spray nozzle clogs, improving line uptime by 25%.
These examples highlight the versatility and ROI of precision monofilament mesh filtration across critical applications.
Summary and Next Steps
Polypropylene Monofilament Mesh Liquid Filter Bags provide unmatched surface‑flow filtration, combining precise pore size control, low pressure drop, and robust chemical resistance. By selecting the correct micron rating, collar style, and maintenance scheme, you optimize system protection, product quality, and operational cost-efficiency.
Next Steps:
-
Assess Your Filtration Needs: Determine required clarity, flow rates, and chemical environment.
-
Select the Ideal Mesh: Choose nominal or absolute micron ratings from 0.5 µm to 200 µm.
-
Verify Housing Compatibility: Match bag size (Size 1 or 2), collar style, and length to your filter vessels.
-
Implement Maintenance Protocols: Establish ΔP monitoring, cleaning, and replacement schedules.
-
Track Performance Metrics: Monitor filtrate quality, ΔP trends, and maintenance intervals to validate ROI and fine‑tune your program.
Investing in the right polypropylene monofilament mesh filter bags ensures consistent, high‑precision liquid filtration—protecting your processes, products, and profitability.
Tags: 0.1 micron filter bag 0.5 micron filter bag 1 micron filter bag 50 micron filter bag 25 micron filter bag 10 micron filter bag 1000 micron filter bag 5 micron filter bag micron filter bag micron filter bags 25 micron filter bags 100 micron filter bag 180 micron filter bag 250 micron filter bag 200 micron filter bag 200 micron filter bags 100 micron filter bags 1 micron filter bags micron filter bags near me 05 micron filter bag 30 micron filter bag 150 micron filter bag 10 micron filter bags 200 micron filter bag wholesale 0.1 micron filter bag wholesale 500 micron filter bag 400 micron filter bag 50 micron filter bag wholesale 400 micron filter bag wholesale 20 micron filter bag 0.1 micron filter bag factory in china 500 micron filter bag factory in china 20 micron filter bag wholesale 5 micron filter bag wholesale 250 micron filter bag factory in china 150 micron filter bag wholesale in china micron filter bag wholesale in china 190 micron filter bag 400 micron filter bag factory in china
Pre:Achieve Pristine Filtration with a 5 Micron Filter Sock
Next:Heavy‑Duty Solids Control with Size #3, 300 Micron Polypropylene Monofilament Mesh Liquid Filter Bag
Tags: